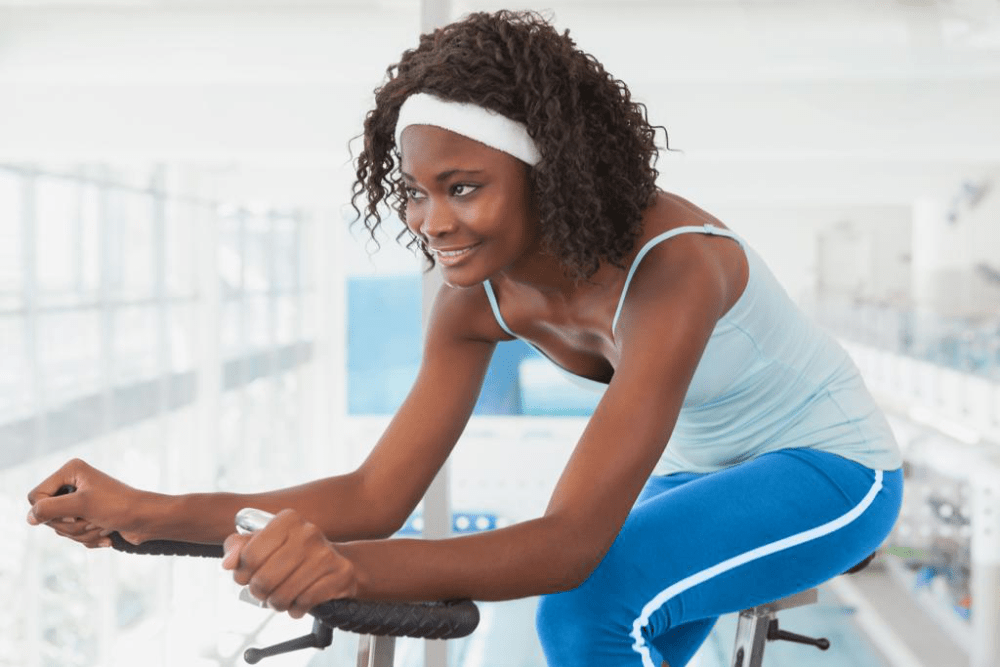
Strength training, also known as resistance or weight training, is a physical exercise designed to enhance muscular fitness.
It targets specific muscle groups by challenging them with external resistance. This resistance could be your body weight or from using equipment like dumbbells, barbells, or weight machines. But strength training isn’t just about growing muscle; it’s a journey of becoming the healthiest version of yourself.
Strength training plays a pivotal role in your overall health and fitness. It’s not just about looking good in front of the mirror (although that’s certainly a perk!). Incorporating strength training into your routine can boost your overall health in a myriad of ways.
We will shed light on the magic of strength training and its benefits, provide valuable insights on how to kickstart your strength training journey and bust some of the myths that might hold you back.
Benefits of Strength Training
A. Improved Muscle Strength and Power
Strength training, as the name suggests, bolsters muscle strength and power. With regular strength training, your muscles learn to work harder, more efficiently, and for a longer duration. This translates to improved performance in the gym and aids everyday tasks such as lifting groceries or moving furniture.
B. Enhanced Metabolic Rate and Weight Management
Strength training is a powerful ally in weight management. It can elevate your metabolic rate, so you’ll continue burning calories even after your workout. More muscle equals more calorie-burning power!
C. Improved Joint Stability and Reduced Risk of Injury
A strength-trained body isn’t just a strong body; it’s a stable and resilient one. Regular strength training can improve joint stability, balance, and coordination, reducing the risk of injuries during workouts and daily life.
D. Increased Functional Capacity for Daily Activities
Stronger muscles and joints translate into better mobility and independence, making everyday tasks like carrying groceries, climbing stairs, or gardening much easier.
Types of Strength Training
A. Bodyweight Exercises
These exercises use your body weight as resistance. They’re versatile, requiring no special equipment, and can be done anywhere. Examples include:
- Push-ups: Great for working your chest, arms, and shoulders.
- Squats: A fantastic exercise to strengthen your legs and glutes.
- Planks: Perfect for improving core strength and stability.
B. Free Weights
The types of strength training equipment aren’t attached to an apparatus. They’re versatile and excellent for functional strength. Examples include:
- Dumbbells: Great for both isolated and compound movements.
- Barbells: Ideal for heavy compound lifts like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses.
- Kettlebells: Excellent for dynamic movements and increasing functional strength.
C. Resistance Machines
These machines provide a controlled environment to work individual muscle groups, which can be especially helpful for beginners or those rehabilitating from an injury. Examples include:
- Leg Press: Target your quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes in a controlled manner.
- Lat Pulldown: Work your back muscles with this popular machine.
- Chest Press: Strengthen your chest and arms without worrying about balancing the weights.
D. Functional Training
This focuses on training the body for activities performed in daily life and can incorporate various elements from bodyweight exercises to free weights. Examples include:
- Suspension Training: Uses a system of ropes to utilise bodyweight exercises, enhancing strength, balance, and flexibility.
- Medicine Ball Exercises: These can be thrown, caught, or lifted, adding an element of dynamism and cardiovascular exercise to your strength training routine.
- Plyometrics: Often referred to as jump training, plyometrics involve explosive movements to increase power.
Designing a Strength Training Programme

A. Setting Goals
Before you hit the gym or start pumping iron at home, ask yourself: “What do I hope to achieve through strength training?” It could be anything from gaining muscle, losing weight, and improving bone density, to increasing overall strength. These goals will guide the structure of your programme.
B. Determining Training Frequency
How often should you train? That depends on your goals and schedule. For beginners, two to three days a week is often sufficient. As you progress, you may wish to increase the frequency.
C. Selecting Appropriate Exercises
The types of exercises you select should align with your goals and target the major muscle groups. A mix of upper, lower, and core exercises is recommended for overall strength and fitness.
D. Determining Sets, Reps, and Rest Intervals
The number of sets and repetitions (reps) per exercise and the rest intervals in between sets can significantly affect your training outcomes. Aiming for 2-3 sets of 8-12 reps with a rest period of 60-90 seconds is a good starting point for general fitness.
E. Progressive Overload and Tracking Progress
Progressive overload is the key to continual improvement. This means gradually increasing the intensity of your workouts over time to challenge your muscles. This could be through adding weight, increasing sets or reps, or reducing rest time. Don’t forget to keep track of your progress!
F. Warm-up and Cool-down Routines
Never skip warming up and cooling down! Warming up prepares your body for the workout, reducing the risk of injury, while cooling down helps your body return to its normal state, promoting recovery.
Nutrition and Recovery for Strength Training
Taking care of your body is paramount to seeing the results of strength training. Proper nutrition, hydration and recovery can significantly enhance your performance and progress.

A. Importance of Proper Nutrition
Nutrition fuels your workouts and recovery. It’s the foundation of your fitness journey. Here’s what you should focus on:
- Adequate Protein Intake: Protein is vital for muscle recovery and growth. Aim to include a source of protein in every meal.
- Balanced Macronutrients: Don’t forget about carbohydrates and fats. Carbs fuel your workouts and help restore glycogen stores, while fats are essential for hormone production and absorption of certain vitamins.
- Hydration: Water plays a crucial role in almost all bodily functions, including energy production and muscle recovery. Ensure you’re well-hydrated before, during, and after your workouts.
B. Recovery Strategies
Training breaks your body down; recovery builds it back up. It’s during rest that your muscles repair and grow.
- Rest Days: Give your body the time it needs to recuperate by taking regular rest days.
- Sleep: Sleep is when a lot of muscle recovery and growth takes place. Try to get quality sleep each night.
- Stretching and Foam Rolling: These practices can improve flexibility and circulation, reduce muscle soreness, and speed up recovery.
- Active Recovery: Light, low-impact activities on your rest days can boost blood flow and aid in recovery.
Sample Strength Training Workout Plan
Here are sample workout plans for beginners, intermediates, and advanced exercisers:
A. Beginner’s Workout Plan
For beginners, the focus should be on learning proper form and acclimating to strength training:
Day 1, 3, 5:
- Squats: 2 sets x 10-12 reps
- Bench Press or Push-ups: 2 sets x 10-12 reps
- Bent-over Rows: 2 sets x 10-12 reps
- Overhead Press: 2 sets x 10-12 reps
- Deadlift: 2 sets x 10-12 reps
Day 2, 4, 6: Rest or light cardiovascular exercises
Day 7: Active rest
B. Intermediate Workout Plan
Intermediate lifters should focus on increasing volume and weight while also beginning to target specific muscle groups:
Day 1: Chest and Triceps
- Bench Press: 3 sets x 8-12 reps
- Incline Dumbbell Press: 3 sets x 8-12 reps
- Cable Flyes: 3 sets x 12-15 reps
- Tricep Dips: 3 sets x 8-12 reps
- Skullcrushers: 3 sets x 12-15 reps
Day 2: Back and Biceps
- Deadlift: 3 sets x 8-12 reps
- Pull-ups: 3 sets x 8-12 reps
- Seated Row: 3 sets x 8-12 reps
- Barbell Curls: 3 sets x 8-12 reps
- Hammer Curls: 3 sets x 12-15 reps
Day 3: Rest
Day 4: Legs and Abs
- Squats: 3 sets x 8-12 reps
- Lunges: 3 sets x 8-12 reps per leg
- Leg Curls: 3 sets x 12-15 reps
- Calf Raises: 3 sets x 15-20 reps
- Planks: 3 sets x 30-60 seconds
Day 5: Shoulders
- Overhead Press: 3 sets x 8-12 reps
- Lateral Raises: 3 sets x 12-15 reps
- Reverse Flyes: 3 sets x 12-15 reps
- Face Pulls: 3 sets x 12-15 reps
Day 6, 7: Rest or light cardio
C. Advanced Workout Plan
Advanced lifters may split their workouts further, focusing on one or two muscle groups per day. They often employ advanced techniques like supersets, drop sets, or pyramids:
Day 1: Chest and Abs
- Bench Press: 4 sets x 6-10 reps
- Incline Dumbbell Press: 4 sets x 8-12 reps
- Cable Flyes: 3 sets x 10-15 reps (superset with push-ups)
- Ab Circuit: Crunches, Leg Raises, and Planks: 3 rounds
Day 2: Back
- Deadlift: 4 sets x 6-10 reps
- Pull-ups: 4 sets x 8-12 reps
- Single Arm Dumbbell Row: 4 sets x 8-12 reps
- Lat Pulldown: 3 sets x 10-15 reps
Day 3: Rest
Day 4: Legs
- Squats: 4 sets x 6-10 reps
- Lunges: 4 sets x 8-12 reps per leg
- Leg Press: 4 sets x 8-12 reps
- Hamstring Curls: 4 sets x 10-15 reps
- Calf Raises: 3 sets x 15-20 reps
Day 5: Shoulders and Abs
- Overhead Press: 4 sets x 6-10 reps
- Lateral Raises: 4 sets x 8-12 reps
- Bent Over Reverse Flyes: 4 sets x 10-15 reps
- Ab Circuit: Russian Twists, Bicycle Crunches, and Planks: 3 rounds
Day 6: Arms
- Close-Grip Bench Press: 4 sets x 6-10 reps
- Skull Crushers: 3 sets x 8-12 reps
- Cable Tricep Pushdowns: 3 sets x 10-15 reps
- Barbell Curls: 4 sets x 6-10 reps
- Hammer Curls: 3 sets x 8-12 reps
- Concentration Curls: 3 sets x 10-15 reps
Day 7: Rest
What to Do to Remain Fit During Strength Training
Here’s how to stay fit and healthy during your strength training journey:
- Consistent Training: Stay consistent with your strength training programme.
- Balanced Nutrition: Ensure you are consuming a balanced diet rich in macronutrients (proteins, carbohydrates, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals).
- Adequate Protein Intake: Protein is essential for muscle recovery and growth. Aim for a minimum of 1 gram of protein per kilogram of body weight daily. You can consume this through lean meats, dairy products, legumes, or protein supplements.
- Hydration: Staying adequately hydrated is crucial. During intense exercise, your body loses fluids and ions through sweat. This loss can impact muscle function and overall performance and, if not properly managed, can lead to dehydration. Consuming drinks like Pocari Sweat can help replenish these lost ions and balance your body’s hydration levels. Pocari Sweat is designed to be easily absorbed by the body, refreshing you and helping maintain optimal physical performance.
Conclusion
Strength training offers remarkable benefits for overall health, from muscle growth to mental well-being. It’s a journey of consistent efforts and personal growth. You can start simply, even from home, and seek professional advice as you advance.
So, why wait? Begin your strength training journey today and become a stronger, healthier version of yourself. Every step you take is progress. Rise, shine, and get stronger each day.